Progress is always a good thing. However, as technology advances, so do fraudsters, challenging security systems. This contributes to improving current methods of combating fraudsters and creating new ones. This article tells you about one of them. The concept of EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) was built in 2013, then modified to meet modern requirements. Thus, EDR has evolved into the extended detection and response concept, or XDR.
What is XDR?
XDR is an open cybersecurity architecture integrating security tools at all levels and bridging visibility gaps. It enables faster and more effective threat detection and response, capturing complete data to make informed decisions. XDR was defined in 2018 and is evolving quite rapidly. While many security experts describe XDR as a more pumped-up version of EDR, XDR still has much more potential than the sum of the tools and functionality it integrates. For example, it offers complete threat visibility, a unified interface, and streamlined workflows. One benefit is using “native” XDR and “open source” solutions. “Native” involves integrating security tools directly from the solution provider. On the other hand, Open XDR integrates all the security tools in an organization’s security ecosystem independently of the vendor. In any case, native solutions must also be open to integrating third-party tools.
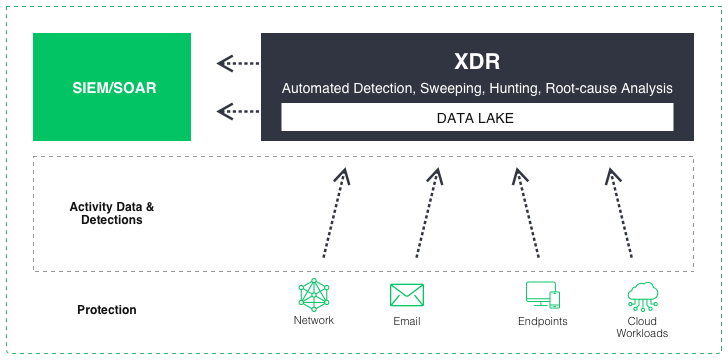
The simplest XDR diagram
How does it work?
XDR connects data from different security solutions to interact and improve threat visibility, reducing the time needed to spot and respond to an attack. XDR provides advanced investigation and threat-hunting capabilities across multiple domains through a single console interface. While often used as a cloud-based service, XDR can also operate as a software-as-a-service. In addition, it can also be the underlying technology behind a Managed Detection and Response offering from a cloud or security solution provider. Simply put, XDR works as follows:
- Loading: It accepts and normalizes volumes of data from endpoints, cloud workloads, identity, email, network traffic, virtual containers, and other sources.
- Detection: It parses and correlates data to automatically detect covert threats using artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Response: It prioritizes threats by severity so that threat hunters can quickly analyze and trace new events and automate the investigation and response process.
In addition, XDR security solutions can integrate the following:
- Personal security tools include antivirus, user and entity behavior analytics, or firewalls.
- Infrastructure-specific security solutions include EDR, endpoint protection platforms, network-level detection, and response, or network traffic analysis.
- Solutions that collect data or coordinate workflows between security layers, including security information and event management systems.
Below, we will look at this integration in more detail.
Continuous data collection
First, XDR collects log and telemetry data from all integrated security tools, creating a continuously updated record of events in the infrastructure. Then, the data is normalized and stored in a central database in the cloud or data warehouse. Each endpoint, regardless if it is a workstation, a server or an IoT element, receives its “footprint” of normal activity. Such a detailed scanning is needed to be able to detect the malignant activity on the earliest stages simply by detecting the unusual actions.
Real-time analysis
XDR uses analytics and machine learning to identify threats and suspicious activity in real time. It does this by analyzing the data, correlating it to threat information, using databases like MITRE ATT&CK. XDR also compares current and historical data and distinguishes real threats from false positives. Finally, the analysis results are displayed in a central management console where the security team can investigate and take action to eliminate hazards.
Automated detection
Automation is what makes rapid response possible in XDR. Based on predefined rules established by the security team or learned through machine learning algorithms, XDR automates the response to threats, enabling rapid detection and resolution of problems and allowing security analysts to focus on more important work. For example, XDR automates the following tasks:
- It prioritizes alerts based on their severity level.
- Disconnecting or shutting down devices, logging users off the network, stopping system/application/device processes, and disabling data sources.
- Launch anti-malware software to scan other devices on the network for threats.
- Triggering relevant SOAR-automated incident response scripts (workflows that automate multiple security products responding to a specific incident).
- In addition, XDR can automate threat investigation and troubleshooting processes. As a result, it enables security teams to respond to incidents faster and prevent potential damage.
Threat investigation and remediation
Once a security threat has been highlighted, XDR allows security analysts to investigate threats, identify their root causes, and remediate them. This process includes destroying malicious files, repairing corrupt configurations, applying updates, and updating detection rules.
Support for threat hunting
Threat hunting is a proactive security analyst exercise that looks for unknown or undetected threats on a network. XDR provides analytics and automation for detecting and responding to threats, including tools for finding threats. As a result, it can reduce detection time and damage from attacks.
Benefits of XDR
Increasingly, organizations are facing severe attacks that bypass prevention measures. As a result, the threat may reside on endpoints and remain on the network for extended periods, gathering information and preparing for a large-scale attack or data breach. While every organization that cares about the security of its data has tools to combat cybercrime, sometimes these tools may work separately, making it difficult to detect and respond to the threat. However, implementing advanced detection and response (XDR) solutions can reduce attack detection time and remediation costs. According to statistics, organizations with XDR reduced the lifecycle time of data breaches by 29%. In addition, they reduced remediation costs by 9% compared to organizations without XDR.
XDR vs EDR
As mentioned earlier, XDR represents an evolution of threat detection and response methods beyond the current point solution and single vector approach. In addition, there are some limits to applying EDR and NTA methods. For example, EDR is limited in detecting and responding to threats only within managed endpoints. This severely narrows the scope of threat detection and the view of who and what is exposed. These limitations ultimately reduce the effectiveness of the response within the SOC. Similarly, NTA tools are limited to monitoring only the network and its segments. Consequently, the multiple logs generated by NTA solutions require a correlation between network alerts and other action data to extract meaning and gain value from network alerts.