Coin mining trojans appeared not so long ago, getting the fame of “not so dangerous virus”. In one of the previous articles, I mentioned the trojan miner as one of the most active trojan types nowadays. But they are too interesting for me to explain them in a couple of sentences. In this article, you will see the reasons for their appearance and main functionality. We will figure out the real harmfulness of coin miner malware.
Milestones in history
The reasons for the appearance of trojan miners are quite obvious when the initial cause is explained. Bitcoin is not a simple cryptocurrency, but while there was no hype in the media, it was not interesting for people. When the first crypto rush started in 2013, more and more people got interested in an equity unit that can grow by 20-30% per month. Later, the Bitcoin price surge gave a punch to the appearance of other cryptocurrencies. Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple, and many others are the products of Bitcoin popularity. They appeared as a BTC substitution, promising to be way more convenient in everyday usage. However, some of them attracted the attention of less legitimate folks.
Big money that rolled in the cryptocurrency environment attracted even bigger money. And where the big money is rolling, individuals or groups of ones who want to have a bite of this bankroll using the outlaw methods are present, too. There are two ways of earning cryptocurrency. The first one supposes receiving payments in coins for the goods or services you sold. Another way is mining the cryptocurrency blocks, getting a commission fee for each mined block. Shopping fraud with cryptocurrencies as a payment method can be pretty profitable, but it is hard to automate. Meanwhile, mining has no problems with it.
Malicious cryptomining explanation
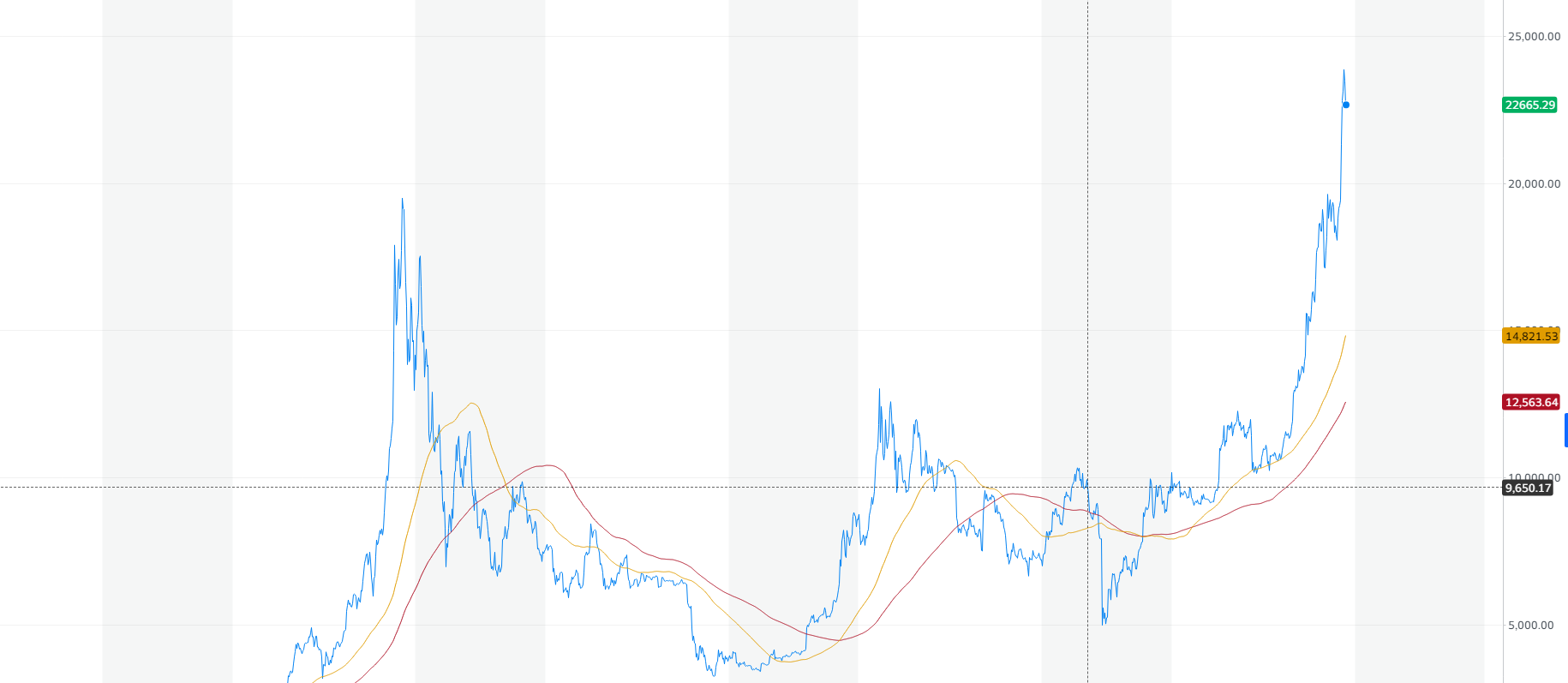
Why do you need to purchase an enormously expensive mining farm, when you can just inject a virus into hundreds of other computers and use them as your own farm? Pretty logical solution and cybercriminals think so as well. The graph below shows the comparison of coin miners’ activity depending on the price of Bitcoin. After a while, it has become something like the main index for the whole cryptocurrency market. The curve shows the clear correlation of trojan-miners spreadness with the cryptocurrency prices.
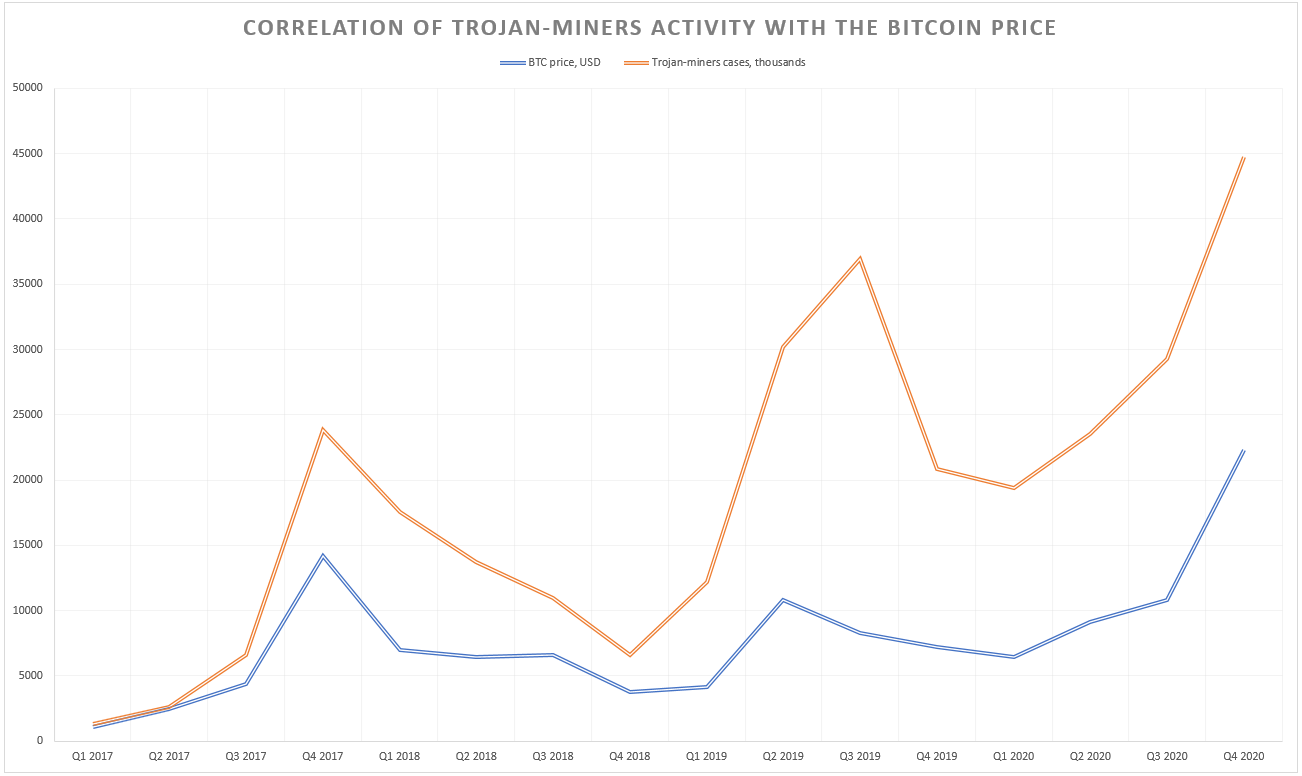
After Bitcoin price sheds, which happened multiple times, coin mining trojans lost their popularity. Since 2019, when the two large spikes in Bitcoin price occurred, coin miners turned on, and in 2020 they showed a new activity peak. In 2022, as cryptocurrencies faced a bear market, miners became less active as well. Still, the price of Litecoin and Monero is 2-3 times higher than it used to be during past bear markets. These coins are famous for very fast and easy mining, so even CPU mining is possible. Cybercriminals who spread coin miner malware usually opt for them when establishing the botnet.
Types of trojan-miner
Trojan miners divide on two separate categories – desktop and in-browser. The names of these types describe themselves: one launches together with your browser, and another starts in your system, regardless of the other running programs. Hence, you can witness the effects of this trojan exactly after the Windows launch, or after the browser launch. The in-browser type is the most popular for some reasons, having about 72% of total trojan-miner detections.
Why are they dangerous?
A lot of people think that coin miner malware carries no real danger for their PCs. Really, the only thing coin miner creates is high CPU/GPU load. “Computer is just a bit of silicon on a PCB. What can go wrong if the components are working on their near-peak performance for some time?”. Unfortunately, such actions can break something important. The programs, that may use a large part of your hardware capacity, are switching the loaded devices dynamically. Therefore, the chance that one of the modules will stop working is minimal. However, trojan-miners do not care about your processor or graphic card. They will load your hardware as hard as they can because their task is to mine the coins. They do not aim at keeping the victim’s PC working properly.
Overheating the processor may lead to its excessive wear. It is especially critical for laptops – they rarely have enough room inside to provide proper cooling. GPUs have an even worse impact upon their performance. Some models can lose over 20% of their performance in just 1 month. Overloads that are usual for the trojan miner activity are more similar to loads during different benchmark tests1. They suppose running the CPUs on the limits of their abilities. Some things may be said about the GPUs, which are usually used on mining farms due to the specific features of graphics processors.
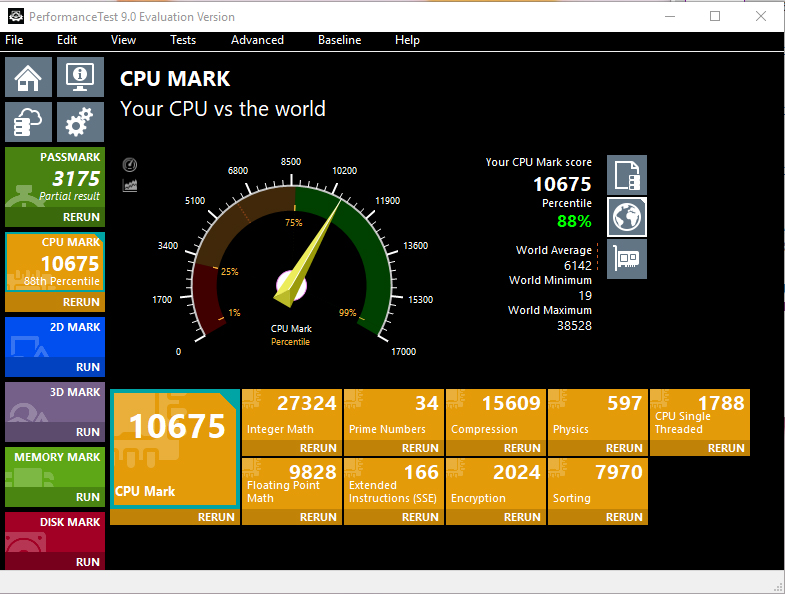
As you can see, coin miners can make much more serious hazards. While other viruses create intangible effects (which can still be priced in dollars), this type of trojan virus can break your computer physically, so neither anti-malware software nor Windows reinstallation will help. The best solution is to delete the trojan miner as soon as possible.
How did I get this virus?
There are many ways of getting infected with the trojan miner. In contrast to ransom trojans, that are used to deploy ransomware and other viruses, they are usually delivered by the variety of trojan viruses2. And the most popular methods for so-called trojan-downloaders are cracking programs (KMS Pico, KMS Tools, and others) and different dubious programs that are stated as “system optimizers” or so. A less popular method of coin miner injection is adware bundle, which contains this virus as a component of a big pack of malware.
Both of these ways are extremely easy to avoid. To be safe for trojan miners, do not use any untrusted utilities, especially if your antivirus program shows you notifications that this tool is possibly dangerous. Adware injection usually happens after clicking the advertisement somewhere on the Web. Installing AdBlock and cutting the habit of clicking the bright and blinking ads on different websites will secure you from this source of malware injection.
How can I remove the trojan miner?
Manual coin miner removal is likely impossible, despite the ease of this operation at the first sight. The trojan-downloader which injected the trojan-miner will just recover the last one if you try to delete the .exe file. Miners that are distributed inside of the adware bundle usually can recover themselves, thanks to the special module built in every such virus. To be sure that nothing excessive uses your hardware, you need to utilize the antivirus tools.
I’d recommend you to use Loaris Trojan Remover. It was originally created to deal with trojan viruses, so this one will not be a problem for it.
 Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
Is a real RED light for the different kinds of spyware
After the installation, run Loaris and launch the full scan. It may last for 10-15 minutes, so be patient
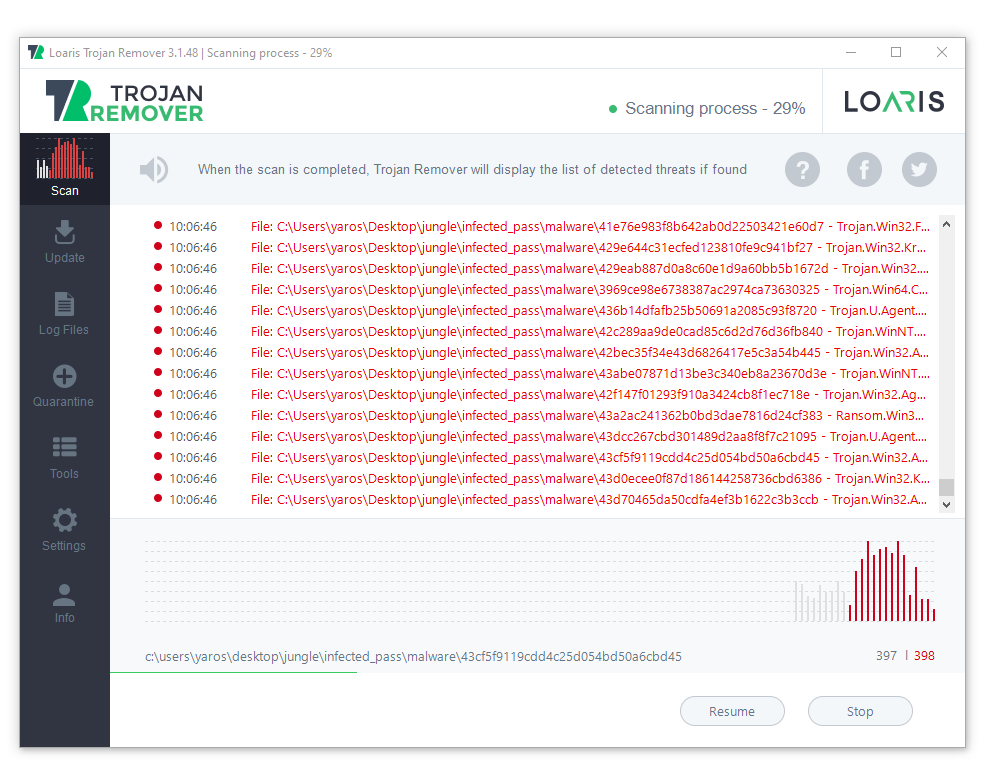
When the scan is finished, press “Apply” to delete all detected viruses. Be sure, the trojan miner will be wiped out, and nothing will menace your PC.
- More details about the benchmarking and stress-testing
- More about the trojan viruses